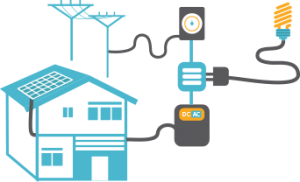
 Types of Solar Rooftop Power Systems
Types of Solar Rooftop Power Systems
A typical rooftop solar power system has electricity-generating photovoltaic panels, commonly known as solar panels, on top of a house or building. But there is much more to it.
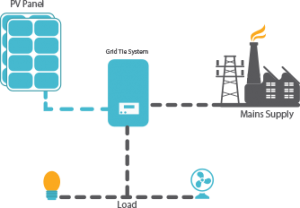 On-Grid System or Grid-tied System
On-Grid System or Grid-tied System
These systems are designed to work in conjunction with the grid or simply put your electricity supply. The electricity you generate using this system is fed back to the grid. A net meter is installed along with this system to keep track of the electricity consumed by you versus what you generated and fed back to the grid resulting in savings which gets reflected in the bill. It does not work when the grid is down.
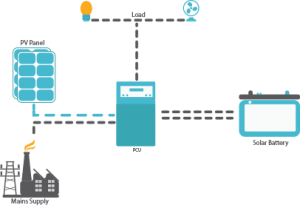 Off-Grid System
Off-Grid System
These systems store the electricity produced by conversion in batteries and utilise the stored energy by converting it back to AC as and when required. The rising cost of other power sources and the increasing demand of electricity, especially in high power cut or no grid areas, has resulted in increased demand for such systems. The reduction in battery prices over the years has further brought the system cost down.
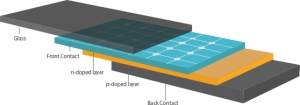 What is a Rooftop Solar Power System all about?
What is a Rooftop Solar Power System all about?
Solar panel is comprised of multiple PV (photovoltaic) cells that convert sunshine to electricity. Two types of PV Panels are there – while one comprise of “Polycrystalline Cells”, the other one contains “Monocrystalline Cells”. Polycrystalline cells are effectively a slice cut from a block of silicon, consisting of a large number of crystals. They have a speckled reflective appearance and are very thick. They are less expensive to produce and more suited for Indian conditions. Monocrystalline cells are cut from a single crystal of silicon- they are effectively a slice from a crystal. In appearance, they have a smooth texture and you will be able to see the thickness of the slice. These are slightly expensive to produce. Based on the area available for solar installation, the required capacity of solar panels can be calculated. Call our solar expert to know your solar potential and get your solar journey started.
 Inverter:
Inverter:
After solar panels, the most crucial component of a residential solar power plant is an inverter. It acts as an interface which converts power produced by solar panels into electricity, that can be consumed by appliances. The type of inverter being used depends on the kind of solar power system you are going for. Grid tie solar power systems need high efficiency power inverters that can feed power from solar panels directly to grid for optimising its performance. They are designed to quickly disconnect from the grid if the utility grid goes down (anti-islanding) as a safety feature for the linesman working on the grid. Another kind of high efficiency solar inverters are there for the off grid solar power system that can charge batteries both from solar and grid power. The inbuilt MPPT (Maximum Power Point Tracking) charge controllers in some good quality inverters extract up to 30{4f4d3157743a2077feee64b71fb582234978d4a84347d02102ed6c3061ea849a} more power from solar panels.
 Mounting Structure:
Mounting Structure:
It is the most critical part as it acts as the skeleton for the entire system, a sturdy structure will result in years of power generation as it needs to withstand strong winds and other natural forces. The type and orientation of the structure varies to a great degree depending on multiple factors associated with the location where the solar power system needs to be deployed. The structure for rooftop solar installation on a flat roof is completely different than that for a slanted roof. The height of your roof is another major factor which determines the composition and alignment of the structure. The quality of the material used has to be as per the MNRE (Ministry of New and Renewable Energy) specified norms. The structure needs to be made of galvanised iron, which is anti-corrosive making the solar power system last long.
 Cables:
Cables:
You can’t use any regular cable for your solar power system. Specialised cables custom made for residential solar power plants are used to ensure minimal loss of electricity being generated. They are UV protected, strong and long lasting enough to withstand the rigours of nature – be it peek summers, incessant rains or thunder storms. Use of any ordinary cable is a big safety hazard with high chances of electrocution for the people in vicinity of the system. Bad quality wire will make you system ineffective and more expensive .
 Peripherals:
Peripherals:
These are the elements which are essential for proper functioning and safety of the system. No compromise must be made on their quality or it will jeopardise the entire solar power system. In terms of their functioning, while Junction Boxes are used to conceal the wiring connections all across the system, Conduits on the other hand are used to protect the wiring of the solar power plants, they can be rigid or flexible or a mix of both based on the requirement. Lightning Arrestors are deployed to save the entire set up in case of lightning strike, especially during monsoon while Earthing, which is a grounding system connecting the residential solar power plant to earth, is done in order to give passage to excess electricity during lightning strike and safeguarding the entire system in the process.
 Batteries:
Batteries:
Apart from these, if you are going for an off grid solar solution, solar batteries are one of the crucial components as they allow you to store the electricity generated by the solar plant and use it in case of power outages or in case of no mains. A good battery would be the one which gives long back up and requires very less maintenance (less frequent water top-up).
Installation:
Lastly, but most importantly the installation of the solar power system needs to be done with precision in order to generate maximum electricity through the solar power plant. No two rooftops are the same therefore the process requires system design and careful supervision to ensure proper installation of the solar rooftop power plant. Solar panels used in any solar power system should be installed facing South direction. Tilt angle of solar panel should be between 8 to 33 degree in India, but it varies as per the height of the installation. Solar panels must be grouted using anchor bolts or concrete foundation to ensure durability in rough conditions. UPS and batteries must be installed as close to the panels as possible to minimize DC transmission losses. One needs to ensure that the maximum permissible voltage is not exceeded when connecting the panels in series. There should be a minimum gap of 5 mm between two solar panels to allow for any expansion in materials. The solar panels being interconnected must be of the same type (mono or poly) and same power class. There should be no shade or shadow on the solar panels as this may lead to losses, formation of hotspots, etc.

